With the arrival of spring, we must consider the processionary moth, in addition to some toxic plants, among the greatest risks to the health of the dog. This dangerous insect for the dog mainly nests in trees such as pine and oak.
The processionary moth is a particularly harmful insect for dogs, but only when it is in the larva stage. It is also dangerous for plants and people.
What is the processionary moth?
The first heat arises problems related to the invasion of harmful insects such as the processionary moth, an insect belonging to the Lepidoptera family, scientifically known as Thaumetopoea. It owes its common name to the single file arrangement adopted when it moves in groups in search of leaves to feed.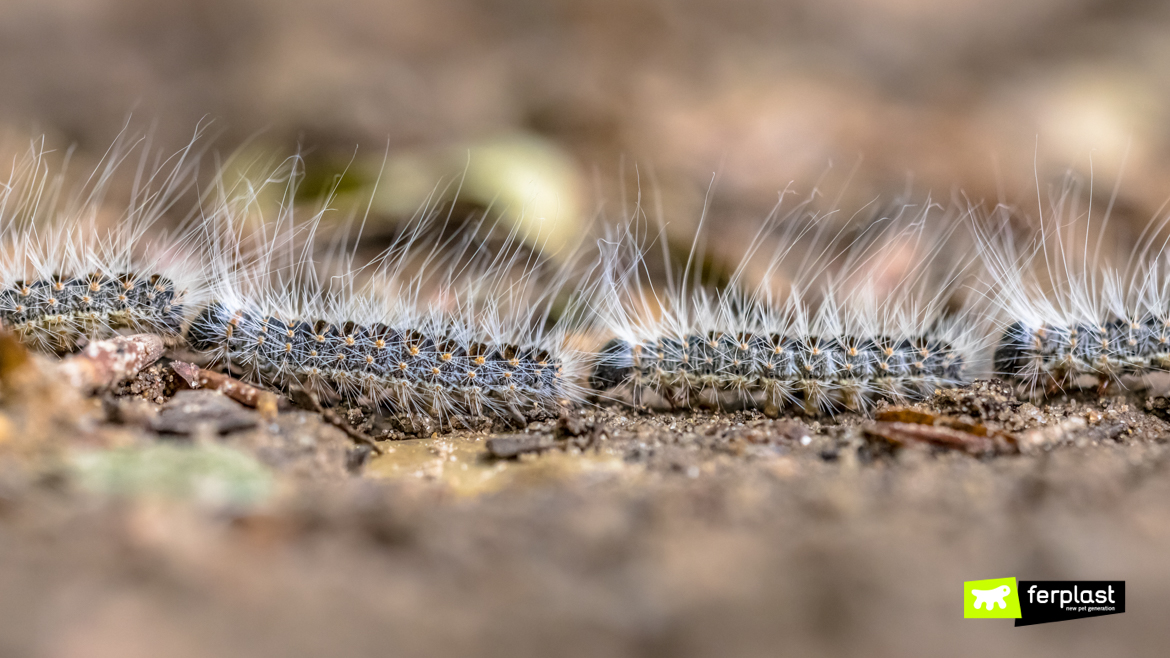
Characteristics of the processionary moth
Young specimens of processionary moth appear as 3-4 centimeter larvae. The larvae have stinging hairs that detach with the wind or upon contact with the animal. In the adult stage, however, the processionary moth turns into a kind of moth and stops being dangerous for dogs. The metamorphosis takes place underground. In the larva stage, the processionary moth passes from leaf to leaf in search of nourishment. These are very voracious specimens, which is why their presence on pines and oaks causes a weakening of the plants. Between April and May the larvae descend from the trees to find a suitable place for transformation.
Why the processionary is dangerous for the dog
What makes the processionary moth dangerous for the dog is the stinging hair. Their inhalation or ingestion can inadvertently occur during walks, while Fido sniffs the ground and explores the territory. The risk of contact with the mucous membranes is very high and is what creates the most serious health problems.
Effects of processionary moth in dogs
The effects of stinging hairs are immediate. The first symptom is abundant and sudden salivation, followed by swelling of the tongue. If immediate action is not taken, the dog may choke or lose part of the tongue that is prone to necrosis due to the severe inflammation. Other symptoms are fever, lack of appetite and diarrhea, or, in case of inhalation, breathing difficulties.
What to do after contact with the processionary
If the dog has come into contact with the processionary moth, it is necessary to react promptly by washing the affected areas with a solution of water and bicarbonate. In case of ingestion, wash the mouth repeatedly, taking care not to touch the stinging hairs with your hands. In this way the stinging substance is removed from the animal. After that it is essential to take the dog to the vet to ascertain the real health conditions.
The processionary moth can be harmful to animals, plants and people. To defend yourself from danger it is not recommended to take any action by yourself. In case you discover a processionary nest it is good to inform the competent local bodies for a remediation and disinfestation intervention.

